Jump
This numbered Frameworks Page covers a single Visual Knowledge Model (VKM). Refer to Tags at the bottom for content classification and source publication if any. The page may be updated to connect with newer Frameworks Pages. The number is for pages, not for content.
Published on March 16, 2014 | Last Updated on September 20, 2025
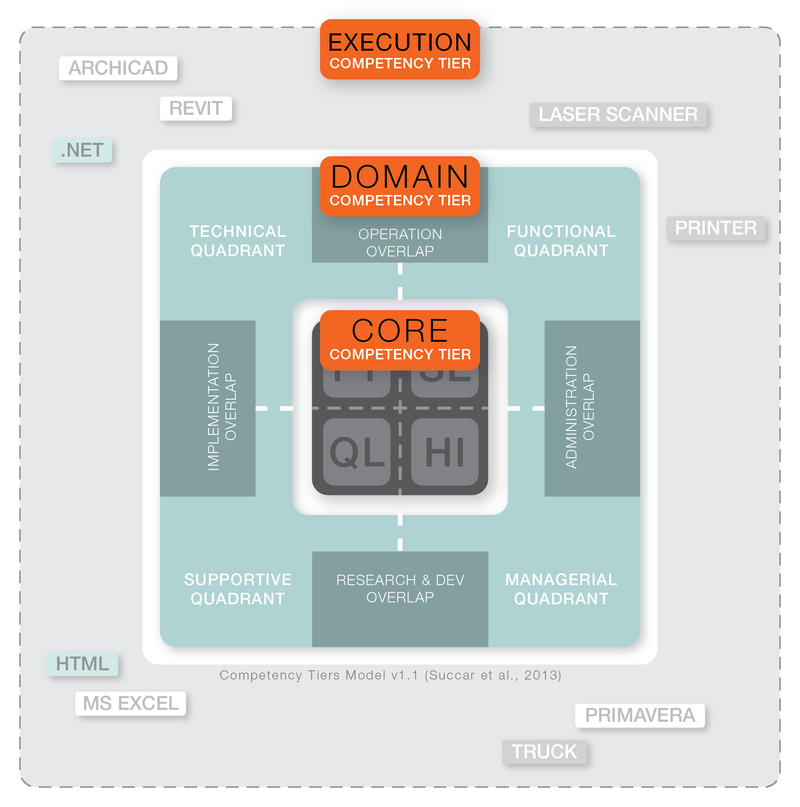
There are three Competency Tiers within the Competency Hierarchy – Core, Domain and Execution:
- The CORE Competencies Tier reflects the personal abilities of individuals enabling them to conduct a measureable activity or deliver a measurable outcome. This core tier is subdivided into the following four competency sets: Foundational traits – personal attributes inherent in an individual that cannot be acquired through training or education; Situational enablers – personal attributes related to nationality, language and other criteria which may play a relevant role when delivering a service or a product; Qualifications and licenses – personal attributes related to the existence or sufficiency of academic degrees, scientific publications, professional accreditations, trade/skill certificates or licences; and Historical indicators – attributes related to employment history, project experiences (including project types and sizes), roles played and positions held.
- The DOMAIN Competencies Tier refers to the professional abilities of individuals, the means they use to perform multi-task activities and the methods they employ to deliver outcomes with complex requirements. There are eight competency sets within this tier: four primary sets – Managerial, Functional, Technical and Supportive – representing the main types of professional ability; and four secondary sets – Administration, Operation, Implementation and Research & Development – identifying those abilities which are formed by the overlap of primary sets.
- The EXECUTION Competencies Tier represents an individual’s ability to use specific tools and techniques to conduct an activity or deliver a measureable outcome. The ability to use a software tool (e.g. a 3D model authoring tool), drive a vehicle (e.g. a 30 tonne tipper truck) or operate specialized field equipment (e.g. a laser scanner) are examples of execution tier competencies. Also, the ability to employ specialized techniques (e.g. programming, drawing and plastering) is also classified under this tier.
Cite as: BIMe Initiative (2025), '18. Competency Tiers', https://bimexcellence.org/frameworks/competency-tiers/. First published 16 March 2014. Viewed 9 March 2026